What Is the Appendix? Function, Pain Symptoms & When It Becomes Dangerous
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the beginning of the large intestine (colon), located in the lower right side of the abdomen.
While its exact function is unclear, it is believed to play a minor role in gut immunity.
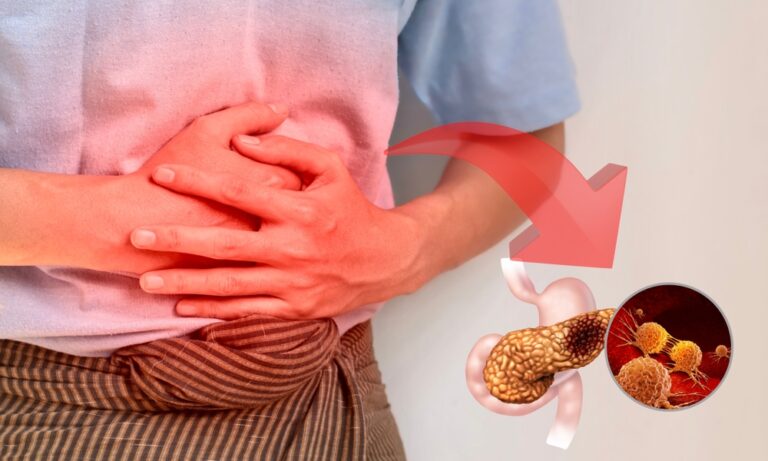
When the appendix becomes inflamed or infected, the condition is known as Appendicitis — a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent serious complications.
What Is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked due to:
- Hardened stool (fecolith)
- Swelling of lymph nodes in the intestines
- Infection or inflammation in the digestive tract
This blockage causes bacteria to multiply, leading to pain, swelling, and infection inside the appendix.
If left untreated, the appendix can burst (rupture), spreading infection throughout the abdomen — a life-threatening emergency.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
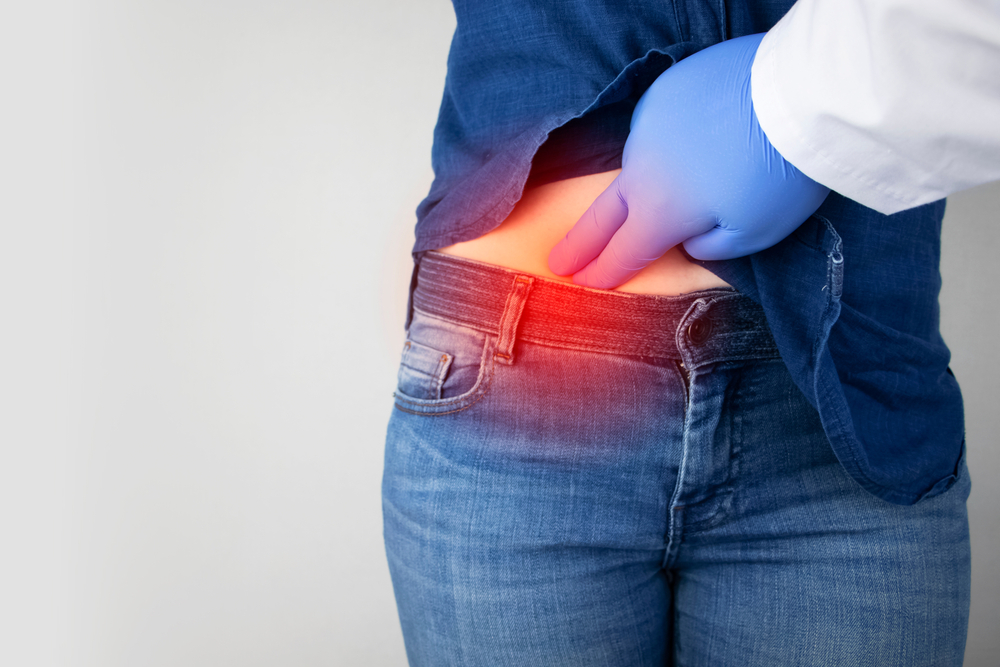
- Sudden pain in the lower right side of the abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and weakness
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Abdominal tenderness that worsens with movement, coughing, or walking
Pain from appendicitis usually begins near the navel and shifts to the right lower abdomen within hours.
Investigations for Appendicitis
Timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial to avoid complications.
Your doctor may recommend the following investigations:
1. Clinical Examination
A detailed history and abdominal examination to check for pain, tenderness, and muscle guarding.
2. Blood Tests
To detect signs of infection, elevated white blood cell (WBC) count.
3. Urine Test
To rule out urinary tract infection or kidney stones.
4. Ultrasound Abdomen
A non-invasive imaging test that helps visualize an inflamed appendix.
5. CT Scan Abdomen
Considered the most accurate test to confirm appendicitis, especially in adults and complex cases.
Complications of Appendicitis
If appendicitis is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious and life-threatening complications, including:
- Perforation (Ruptured Appendix) – The appendix bursts, spreading infection in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
- Appendicular Abscess – A pocket of pus forms around.
- Sepsis (Blood Infection) – Bacteria from the spread into the bloodstream.
- Intestinal Obstruction – Due to inflammation and swelling around the intestines.
Early surgical treatment prevents these dangerous complications and ensures complete recovery.
Best Treatment for Appendicitis
The only definitive treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix, called an Appendectomy.
Delaying surgery increases the risk of rupture and serious infection.
There are two main surgical approaches:
1. Open Appendectomy
A single incision is made in the lower right abdomen to remove the appendix.
While effective, this method involves more pain, longer recovery, and a visible scar.
2. Laparoscopic (Keyhole) Appendectomy – The Best & Modern Treatment
Laparoscopic Appendix Surgery is now the gold standard treatment for appendicitis.
It is a minimally invasive, safe, and painless procedure performed through 3 tiny incisions using a camera (laparoscope) and fine surgical instruments.
The surgeon removes the infected appendix with precision, ensuring faster healing and minimal complications.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Painless and bloodless procedure
- No large incision or scar
- Faster recovery and short hospital stay
- Minimal postoperative pain
- Lower risk of infection
- Quick return to daily activities
- Better cosmetic results
In cases where the appendix has already ruptured, laparoscopic surgery also allows better cleaning of the abdominal cavity, preventing further infection.
Why Choose Laparoscopic Surgery for the Appendix?
Laparoscopic appendectomy offers all the benefits of modern minimally invasive surgery:
- Safe and precise removal
- Short hospital stay (usually 24 hours)
- Early mobilization
- Excellent long-term results
It is the preferred treatment worldwide for both simple and complicated appendicitis.
Conclusion
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that must be treated without delay.
Ignoring symptoms can lead to rupture and serious infection.
The best and safest treatment is Laparoscopic Appendectomy, which ensures quick recovery, minimal pain, and excellent results.
If you experience persistent right-sided abdominal pain, nausea, or fever, consult a qualified laparoscopic surgeon immediately for evaluation and timely treatment.