What Is a Hernia? Causes, Types, Symptoms & Treatment Guide
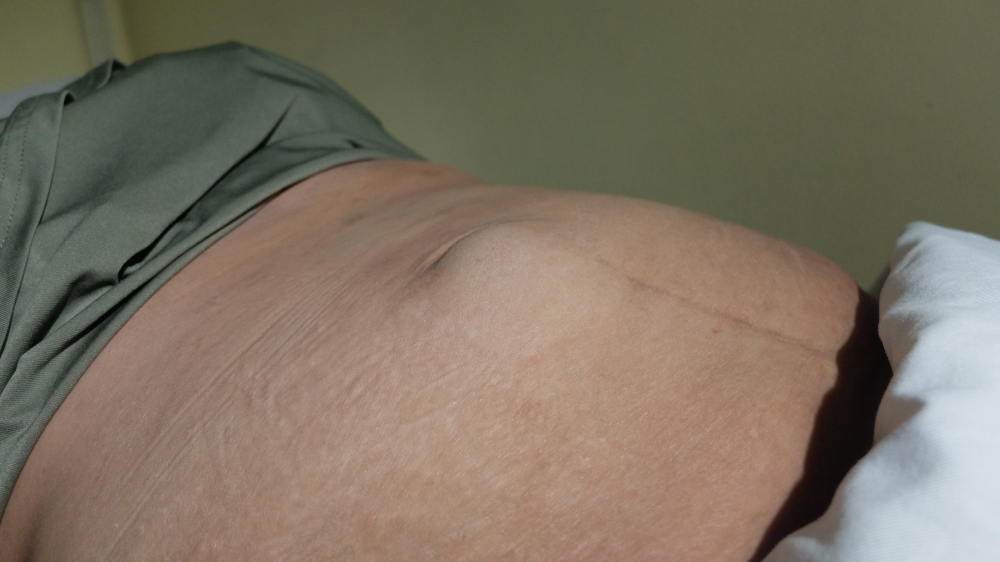
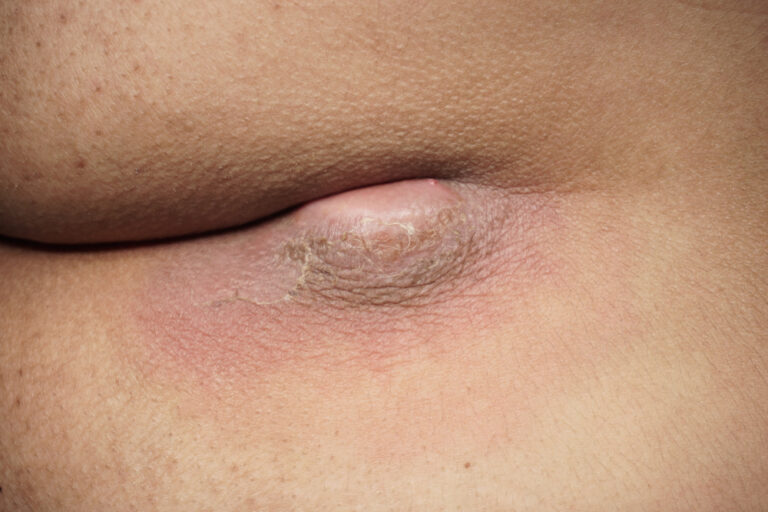
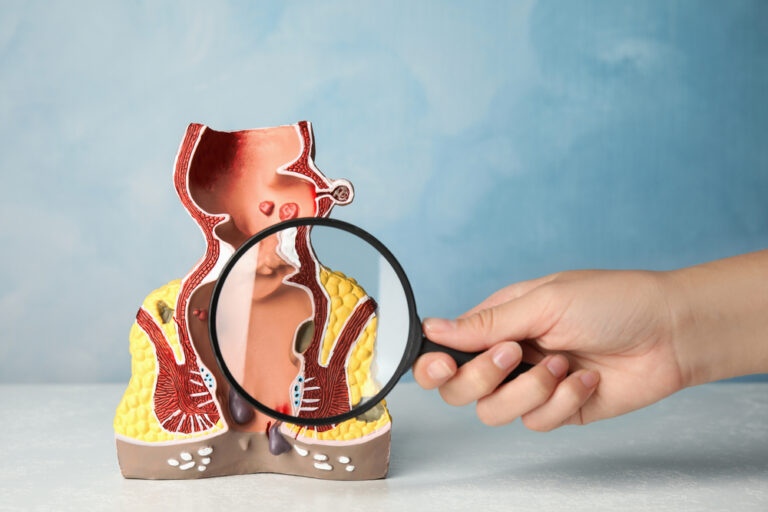
A hernia occurs when an internal organ, most commonly a part of the intestine, pushes through a weak spot in the muscles or abdominal wall.
This creates a visible bulge or lump, which may cause pain or discomfort, especially while standing, coughing, or lifting heavy objects.
It does not heal on its own and often worsen over time if left untreated.
Surgical repair is the only permanent cure.
Common Types of Hernia
- Inguinal Hernia:
Occurs in the groin area and is the most common type, especially in men. - Femoral Hernia:
Found in the upper thigh near the groin — more common in women. - Umbilical Hernia:
Appears near the navel, often seen in infants or overweight adults. - Incisional Hernia:
Develops at the site of a previous surgical scar. - Hiatal Hernia:
Part of the stomach pushes up into the chest through the diaphragm, causing heartburn or acid reflux.
Symptoms of Hernia
- Swelling or a bulge in the abdomen or groin
- Pain or discomfort while lifting, coughing, or bending
- Heaviness or dragging sensation
- Burning or aching at the bulge site
- In severe cases, nausea, vomiting, or constipation (if the intestine becomes trapped — a strangulated )
If you experience sudden, severe pain with vomiting or a non-reducible lump, it may indicate a surgical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Investigations for Hernia
A clinical diagnosis is usually made through physical examination, but your doctor may recommend certain tests to confirm and plan the best treatment:
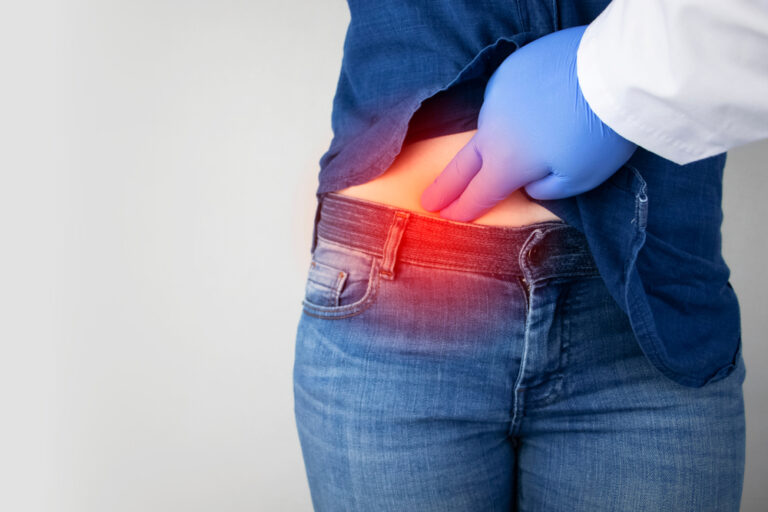
- Physical Examination:
The doctor inspects and palpates the affected area while you stand or strain. - Ultrasound Abdomen / Groin:
Helps detect the hernias and assess their size and contents. - CT Scan or MRI:
Used for complex or recurrent conditions to identify the exact location and muscle weakness. - Endoscopy:
For hiatal to evaluate the upper digestive tract and reflux symptoms.
Best Treatment for Hernia
Unfortunately, cannot be cured by medicine or exercise.
The only effective treatment is surgical repair — either by traditional (open) or modern laparoscopic (keyhole) method.
1. Open Hernia Repair
The surgeon makes an incision over the site, pushes the protruding tissue back inside, and reinforces the weak area with a surgical mesh.
While effective, recovery time is longer and pain is usually greater compared to laparoscopic surgery.
2. Laparoscopic (Keyhole) Hernia Repair – The Best & Modern Treatment
The laparoscopic repair is the most advanced, safe, and preferred method worldwide.
It is a minimally invasive, bloodless, and painless procedure performed using small incisions and a tiny camera (laparoscope).
It is repaired from inside the abdominal wall using a special surgical mesh, which strengthens the weak area and prevents recurrence.
Advantages of Laparoscopic
- Painless and bloodless procedure
- No large cut or visible scar
- Day-care surgery – discharge on the same day
- Quick recovery – return to work within a few days
- Minimal postoperative pain
- Lower recurrence rate
- Both sides (bilateral) can be repaired in a single procedure
This technique is suitable for inguinal, umbilical, femoral, and incisional, and is especially recommended for recurrent or bilateral.
Why Choose Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery?
Laparoscopic repair provides better results, faster healing, and less postoperative pain compared to open surgery.
It is performed under general anesthesia and offers:
- Superior cosmetic results
- Short hospital stay
- Faster return to daily activities
- Minimal risk of infection
It is now considered the gold standard for repair worldwide.
Conclusion
A hernia is a common but potentially serious condition that requires timely surgical repair.
Among all available options, Laparoscopic Surgery offers the best, safest, and most effective solution — ensuring quick recovery, minimal pain, and long-lasting results.
If you notice a bulge or discomfort suggestive, consult an experienced laparoscopic surgeon for early diagnosis and advanced treatment before complications develop.